Governed by business logic and structured inputs, robotic process automation (RPA) is an automation technology that helps organizations to partially or fully automate standardized tasks. Robotic process automation software robots, or “bots” can mimic the actions of humans to perform jobs such as data entry, transaction processing, response triggering and communicating with other digital systems. RPA systems range from simple website “chat bots” that can answer standard queries to deployments of thousands of bots that can automate credit card processing and fraud detection jobs.
Typically, organizations begin with small robotic process automation pilot programs and then move to more comprehensive programs over time. Often, enterprises will bring developers on board to create more sophisticated solutions. These will usually involve implementation of dedicated PCs or virtual clients – increasingly located in the cloud – that are used exclusively by the software bots. These large-scale deployments typically involve hundreds or thousands of software bots to handle vast numbers of routine tasks.
What Does Robotic Process Automation Look Like?
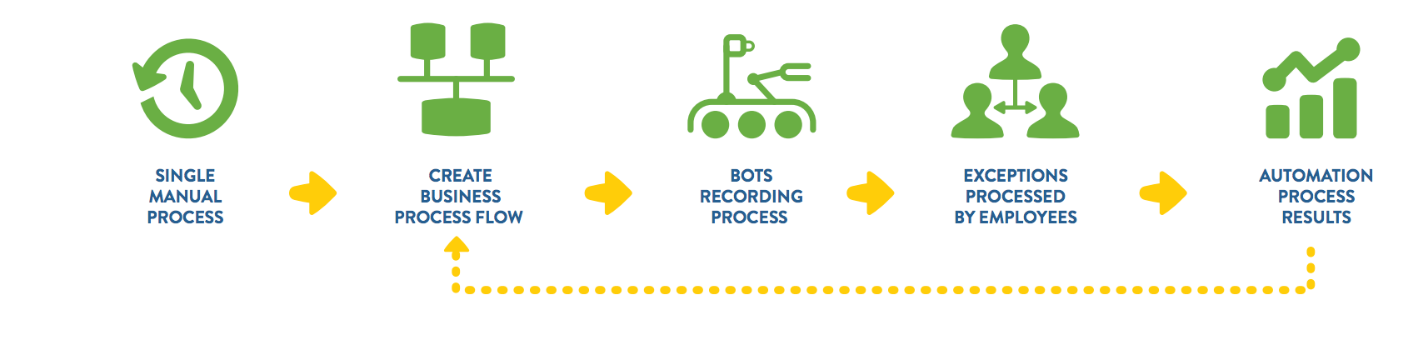
Here is how a typical, repetitive task can be automated with a software bot:
- A single, manual task is used to create a business process flow.
- An RPA bot(s) then records this business process.
- Any exceptions to this process are identified and assigned to humans to manage.
- The robotic process is put into production, on repeat.
- The process is continuously refined through a loop to maximize efficiency and accuracy.
What Are the Key Benefits of RPA?
RPA technologies are meant to enhance – not replace – the human workforce, and can:
- Boost efficiency. RPA helps humans shift focus and resources away from low-value, high-volume tasks such as data entry and focus on ideas, innovation and higher-value work. This, in turn, can help reduce employee burnout and workforce churn.
- Reduce operational risk. By eliminating human errors due to everything from lack of sleep to hunger to carelessness, RPA ensures heightened accuracy and consistency of outputs.
- Reduce costs. RPA speeds transactional work and enhances the productivity of the human workforce – helping organizations do more with less.
- Accelerate scale. Since robots don’t take breaks and can work 24x7x365, processes can be scaled easily across countries and business units or entities.
- Simplify compliance. By minimizing human access to sensitive systems and information, RPA can help reduce a number of compliance and audit challenges and help streamline audits.
According to the Deloitte Global RPA Survey, 2018, RPA can improve workforce productivity by 86 percent, improve quality and accuracy by 90 percent and improve compliance by 92 percent.
What Are the RPA Security Risks?
Despite its many benefits, RPA technology introduces a new cyber attack surface for both humans and non-human identities. This means that RPA security will be of paramount importance.
RPA software bots require privileged access (or “power access”) to perform their required tasks, such as logging into ERP, CRM or other business systems to access, copy or paste information or to move data through a process from one step to the next. This need for constant access means that privileged credentials are often hard-coded directly into the script or rules-based process the bot follows. Or the script may include a step to retrieve the credentials from an insecure location, such as a commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) application configuration file or database
RPA credentials are often shared so they can be used over and over again. Because these accounts and credentials are left unchanged and unsecured, a cyber attacker can steal them, use them to elevate privileges and move laterally to gain access to critical systems, applications and data. Or users with administrator privileges can retrieve credentials stored in insecure locations.
As many enterprises leveraging robotic process automation have numerous bots in production at any given time, the potential risk is very high. Securing the privileged credentials utilized by this emerging digital workforce is an important step in securing RPA workflows.
How to Protect RPA Privileged Credentials
To protect against unauthorized access to, and misuse of, the privileged credentials used in robotic process automation, organizations typically take the following steps:
- Remove privileged credentials from scripts and other insecure locations and store them in a centralized, encrypted location.
- Limit the bots’ access by implementing the principle of least privilege and granting them privileged access only to the specific applications they need to perform their tasks
- Secure RPA console access by managing the credentials leveraged by the RPA admins, as well as isolate and monitor activity and suspend or terminate suspicious sessions to minimize risk.
Learn More About RPA Security Privileged Access Security
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Solving Key Security Challenges in RPA Deployments
- Securing Robotic Process Automation with CyberArk
- Privileged Access Security Best Practices for Robotic Process Automation: CyberArk and UiPath
- Fortune 100 Company Accelerates Operational Agility with Cyberark Blue Prism Integration